Earth is a diverse planet with a variety of landforms, which are the natural features of its surface. These landforms have been created through a combination of geological, biological, and atmospheric processes that have shaped the Earth over millions of years. Let's see about the major landforms of the Earth.
Take a look at the earth on Google Earth click here
The Earth’s landform is the result of two processes.
- Internal Processes.
- External Processes.
Internal Processes include the upliftment and sinking of the earth’s surface at several places.
External Processes such as erosion and deposition. These two processes are carried out by running water, ice, and wind.
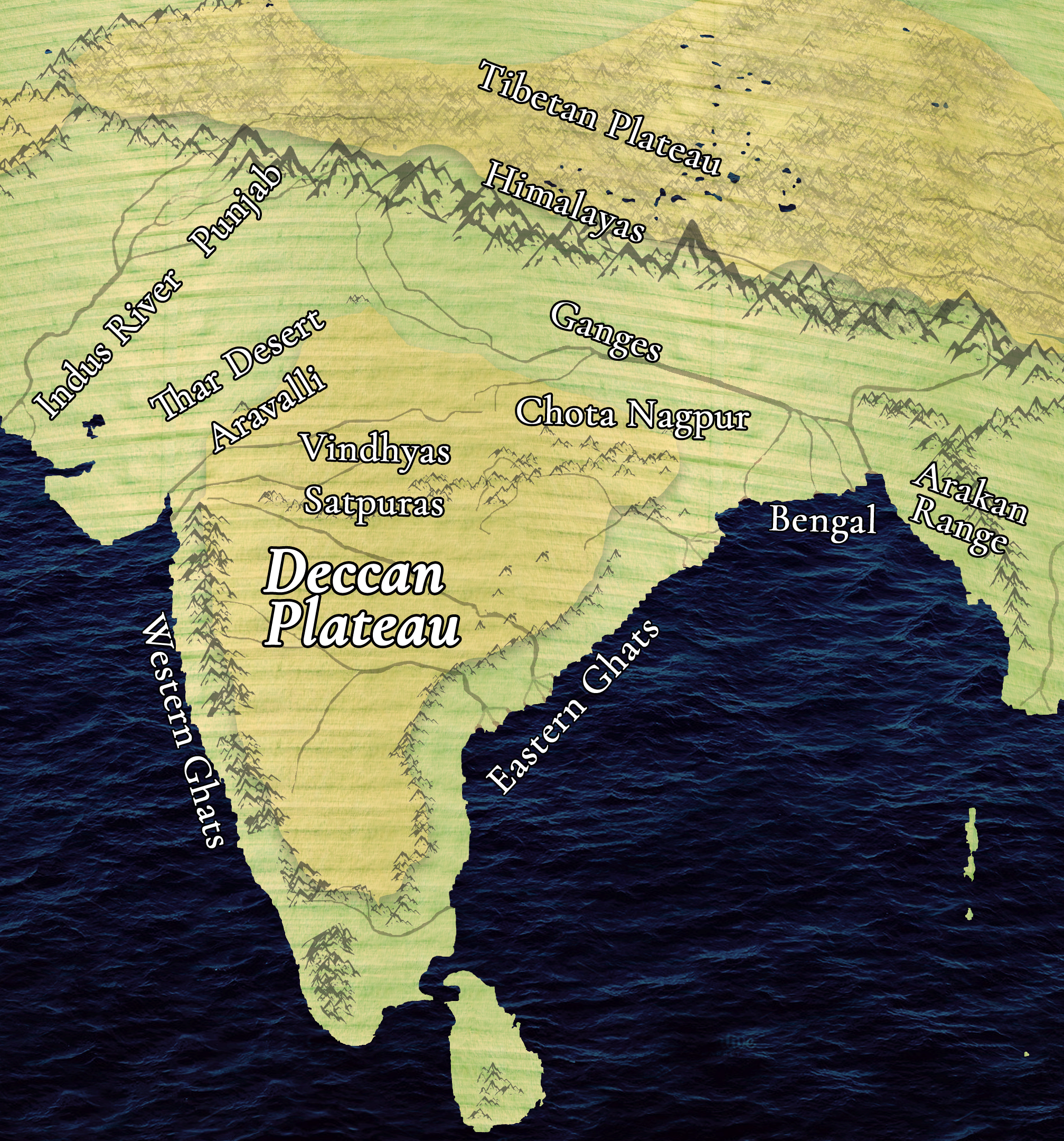
Further, this chapter will discuss different landforms depending on elevation and slope such as mountains, plateaus, and plains which were the major landforms of Earth.
First, we discuss about the Earth's Major landforms Mountains,
MOUNTAINS
A mountain is any natural elevation of the earth's surface. The mountains may have a small summit and a broad base. It is considerably higher than the surrounding area. Mountains have less land for farming.
Mountains may be arranged in a line known as a range. Many mountain systems consist of a series of parallel ranges extending over hundreds of kilometers.
Types of Mountains
- Fold Mountains
- Block Mountains
- Volcanic Mountains
FOLD MOUNTAINS
The Himalayan
Mountains and the Alps are young fold mountains
with rugged relief and high conical peaks.
 |
| The Himalayas |
The Aravali range in India is one of the oldest fold mountain systems in the world.
 |
| Aravali Range |
The Appalachians in North America and the Ural Mountains in Russia have rounded features and low elevation because of erosion over a due course of time. They are old fold mountains.
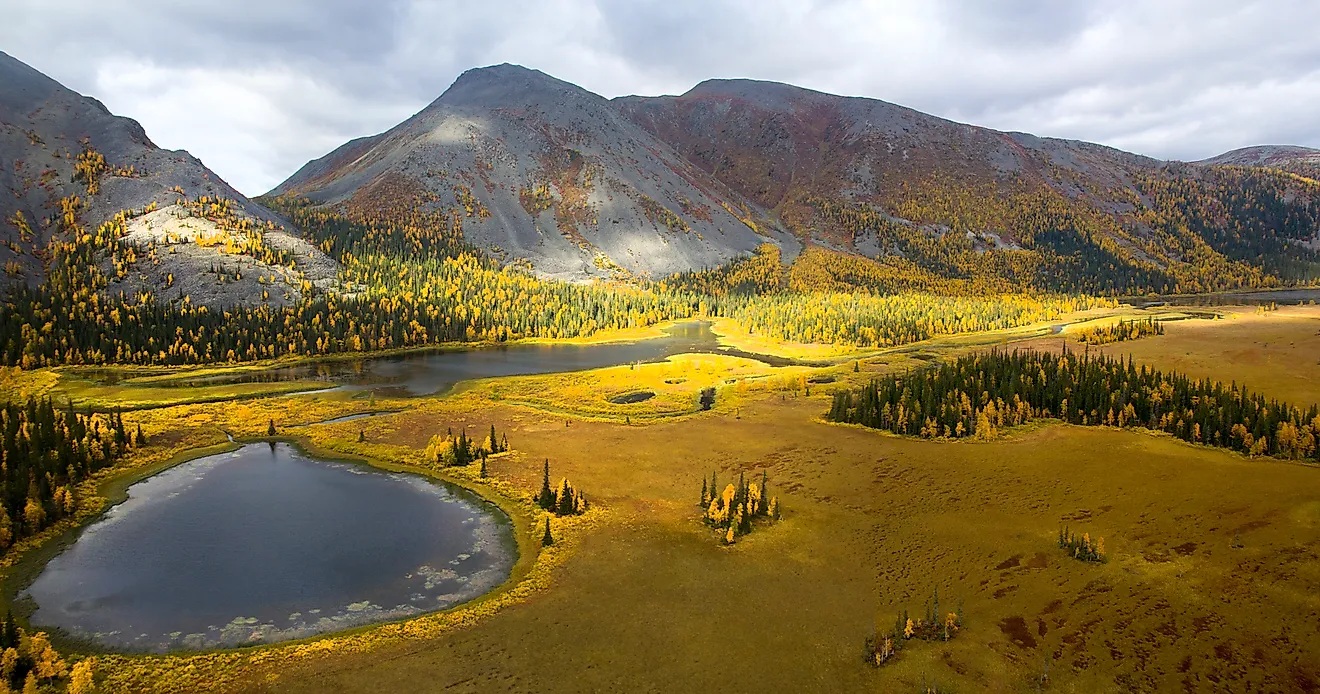 |
| Ural Mountains |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/header-APPALACHIA0722-ea4c6442310d4a4e8e96c24ae3856e25.jpg) |
| Appalachians |
BLOCK MOUNTAINS
Block Mountains are created when large areas are broken and displaced vertically. Mostly
block mountains form valleys on the earth's surface.
The uplifted blocks are termed as horsts and the lowered blocks are called graben.
 |
| Rhine Valley |
The Rhine Valley and the Vosges Mountains in Europe are examples of such mountain systems. Locate them on the world map in the atlas and find out some more examples of this type of landforms.
VOLCANIC MOUNTAINS
Volcanic mountains are formed due to volcanic activity.
 |
| Mt. Fujiyama |
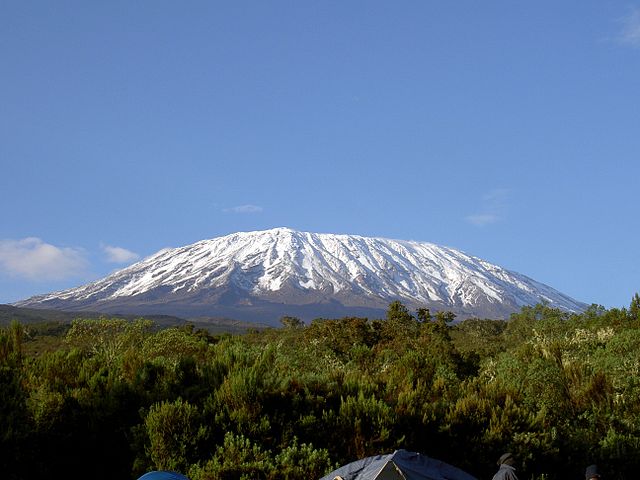 |
| Mt. Kilimanjaro |
USES OF MOUNTAINS
- The mountains are a storehouse of water.
- Many rivers have their source in the glaciers in the mountains.
- Reservoirs are made and the water is harnessed for people's use.
- Water from the mountains is also used for irrigation and the generation of hydroelectricity.
- The river valleys and terraces are ideal for the cultivation of crops.
- Mountains have a rich variety of flora and fauna.
- The forests provide fuel, fodder, shelter and other products like gum, raisins, etc.
- Mountains provide an idyllic site for tourists.
- They visit the mountains for their scenic beauty.
- Several sports like paragliding, hang gliding, river rafting and skiing are popular in the mountains.
PLATEAUS
- The Deccan Plateau in India is one of the oldest plateaus.
- The East African Plateau in Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda and the Western Plateau of Australia.
- The Tibet plateau is the highest in the world with a height of 4,000 to 6,000 metres above the mean sea level.
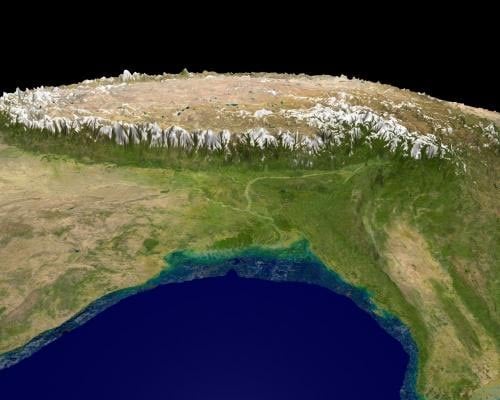 |
| Tibet Plateau |
- The African plateau is famous for gold and diamond mining.
- In India, huge reserves of iron, coal and manganese are found in the Chhotanagpur plateau.
 |
| Hundru Falls |
- In India, the Hundru Falls on the Chhotanagpur plateau on the river Subarnarekha.
- The Jog Falls in Karnataka.
PLAINS
- Asia, these plains are formed by the Ganga and the Brahmaputra in India and the Yangtze in China.
- In India, the Indo-Gangetic plains are the most densely populated regions of the country.
USES OF PLAIN
- Plains have abundant fertility.
- Establishing a transit network is simple.
- The best places for people to live are plains.
- Since more flat areas are available for cultivation and housing construction, there is a greater concentration of people.
- Because of fertile soils, the land is highly productive for cultivation.

.png)